Autism spectrum disorder is the most misconstrued and confusing of neurodevelopmental disorders. Children with this disorder show signs of major deficits in three main areas of development: social interaction, communication and repetitive patterns of behaviours or lack of interests. These deficits appear early in their growing years and cause serious impairments in functioning.
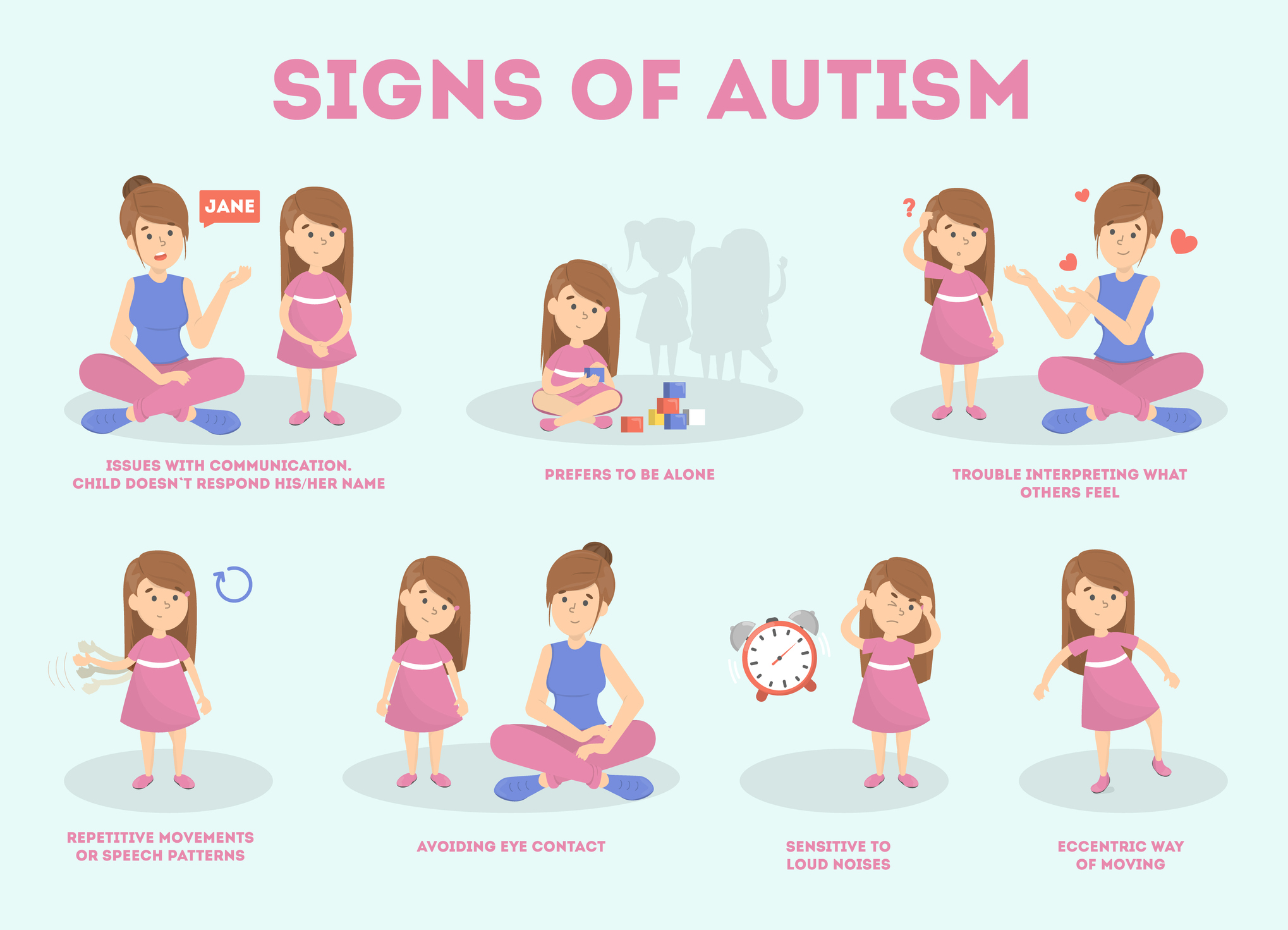
The child with autism might exhibit deficits in social interaction by not initiating conversations with other children or by not making eye contact with them and they prefer playing alone. It is almost as though these individuals live in their own isolated social world.
Communication deficits can range from a complete lack of speech to one-word responses (saying “Yes” or “No” even though they should be replying to questions or statements that require explanation), echoed speech (imitating what another person says, either immediately or several hours or even days later), and difficulty maintaining a conversation because of an inability to reciprocate others’.
These deficits can also include problems in using and understanding nonverbal cues (facial expressions, gestures, emotions and body language) that enable normal communication.
Repetitive patterns of behaviour or interests: the child might engage in stereotyped, repetitive movements (rocking, head-banging, tip-toe walking or repeatedly dropping an object and then picking it up), or might exhibit tantrums at even a small change in the daily routine or the environment.
While people with autism spectrum disorder usually show several of the following:
- Trouble making eye contact
- Difficulty following and engaging in conversations
- Extreme distress or they exhibit tantrums when routines are even slightly interrupted
- Facial expressions that un-match verbal communication
- Intense interest in particular objects
- Show a lack of interest in age-appropriate activities
- Not able to express feelings or needs in words
- Not engaging in “pretend” play
- Sensitivity (hyper or hypo sensitive) to sensory stimuli including taste, light, sound, texture and smell
Repetitive behaviours (elf-stimulating, repetitive behaviours like rocking, walking on toes, head banging or flapping hands)
- From regular developmental check-ups during childhood, doctors track the number of developmental milestones and screen for different types of developmental delays. When children are diagnosed with developmental delay, they may receive further evaluation. Children aged 18 to 24 months can be screened for autism by the screening tools available.
- During an additional evaluation, a group of specialists that may include a developmental paediatrician, a child psychiatrist, and a speech-language pathologist, will assess a number of things including age-appropriate behaviours, cognitive skills, and language abilities.
Diagnosing in Adulthood: Most of the time autism is diagnosed in early childhood but can also be diagnosed during adolescence and adulthood. Diagnosis later in life can sometimes be challenging since some symptoms of autism can be confused with other mental health conditions like anxiety, OCD and ADHD.
While the exact cause is not known, research suggests that there is likely a genetic aspect to the condition. Research shows that children who have a sibling with autism are at a higher risk of having autism.
Types
When an individual is diagnosed with autism, they will also have their functional level identified. These levels are used to describe how severely their behaviours and social skills are affected.
- Level 1: High functioning
- Level 2: Moderately severe
- Level 3: Severe
There is no single mode of treatment that is best. People with autism have a wide range of symptoms. That means each person’s needs are different. Treatment includes various forms of therapy and medications.
Treatment for autism often focuses on behavioural, psychological, or skills training interventions.
One commonly used approach is Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA), a form of therapy that utilizes reinforcements to teach and reinforce desirable behaviours and skills.
Other common therapies used in the treatment of autism include:
- Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT)
- Early intensive behavioural intervention
- Pivotal response therapy
- Relationship development intervention
- Verbal behaviour therapy
- Such therapies are planned in ways to help individuals with autism spectrum disorder to:
- Nurture cognitive abilities
- Improve existing strengths
- Increase language and communication skills
- Improve social skills
- Learn adaptive skills that allow for independent, day-to-day living
Parenting a Child with Autism
Learning that a child has autism can be overwhelming and parents might go through different emotions.
In addition to seeking professional treatment, there are also a number of self-help strategies that parents can use to help cope with some of the symptoms of autism.
- Be accepting
- Create a relaxing and comfortable environment
- Follow a schedule
- Join a support group
- Learn to identify the triggers
- Pay attention to non-verbal communication
- Use positive reinforcements
It’s important to know that autism is a relatively common condition and many resources and professionals are available to help parents provide the best support for their child.
Sana Rubiyana Psychologist & RECBT Therapist: [email protected]


0 Comments